Sample rate
Understanding Sample Rate in Audio
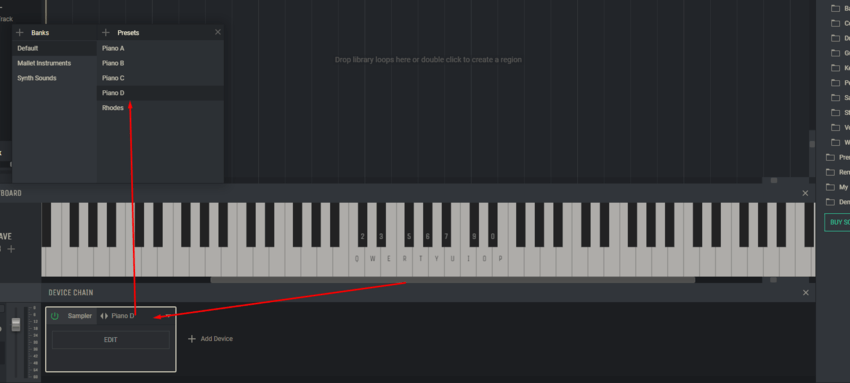
A key conversion occurs in the process of translating sound from the analog form that the microphone picks up into the digital code that the audio workstation processes. Audio interfaces play a critical role in this process, turning sound waves into digital data according to the parameters set in your digital audio workstation (DAW). Setting these parameters correctly is critical as it directly affects the final sound and quality of your track.
Sampling rate is one of the fundamental aspects when converting audio to digital. It determines how often the analog signal is measured during conversion, which in turn affects the accuracy and completeness of the digital representation of the original sound. Choosing the right sample rate allows you to achieve an immersive studio experience while preserving all the depth and nuance of the original recording.
Let’s take a closer look at what you need to know about sample rate to make your music sound magical.
What is the sampling rate for audio?
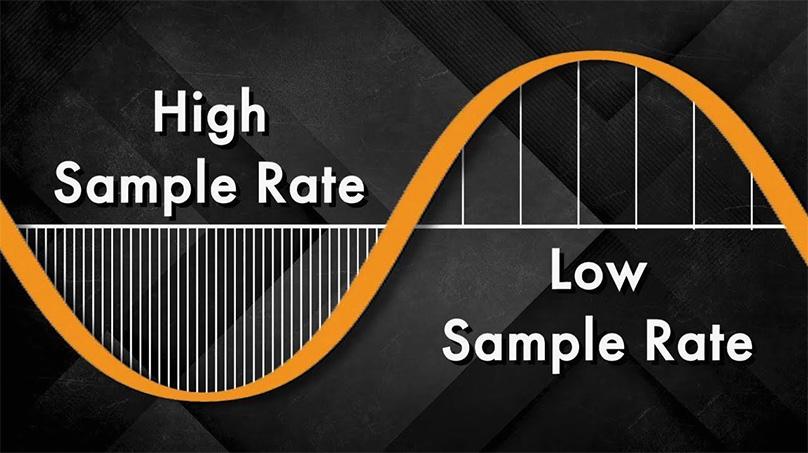
Sampling rate is the speed at which sound waves are captured and converted into digital audio. The higher the sampling rate, the better the sound quality because more sound waves are recorded and converted into digital form. The sampling rate is selected depending on the goals of a particular project. For example, recording audio may require one sampling rate, but storing archival masters or audio files may require another.
In either case, the sampling rate is determined using the Nyquist-Shannon theorem. This principle of digital processing states that in order to correctly convert analog audio into a digital signal, the sampling frequency must be at least twice as high as the frequency of the original sound wave.
For audio processing, a sampling rate of 44.1 kHz is often used because the human hearing range is from 20 Hz to 20 kHz. Therefore, 44.1 kHz is sufficient to reproduce most audible audio frequencies. However, some instruments and sounds may fall outside this range, so it is important to evaluate each situation individually to ensure the best sound quality.
The Nyquist frequency, also known as the folding frequency, is measured from the highest point of the sound wave. 20 kHz is about half the sample rate of 44.1 kHz, allowing most modern recordings to have a sample rate of 44.1 kHz or higher.
Technically, a higher sample rate equals higher quality. However, this does not always mean a noticeable difference in the sound of the audio file. Since the human audible spectrum ranges from 20 Hz to 20 kHz, sampling rates around 44.1 or 48 kHz are usually sufficient for digital audio.
Digital conversion at a higher sampling rate increases the amount of data in an audio file, but also increases the file size. Unless you are preparing audio for special purposes, such as archiving or specialized applications, standard audio sampling rates are usually sufficient for most needs.
What should the sampling rate be – 44.1 or 48?
Many audio professionals still consider 44.1 kHz to be the standard for audio recording. This is because at this frequency it is possible to produce high-resolution audio without overly taxing the processing power available to most consumer processors. However, in professional audio recordings are typically used at 48 kHz to provide additional precision across the entire frequency spectrum.
It’s worth noting that popular streaming platforms like Spotify use 44.1 kHz by default. For streaming, CDs and MP3s, 44.1 kHz remains the gold standard. However, for professional audio applications such as video and DVD, 48 kHz is the standard.
Ultimately, the sampling rate must match the target audio output and the environment in which it will be used.
Bit Depth vs. Sampling Rate: What’s the Difference?
You will often hear that sample rate is related to bit depth. Although both of these parameters are important for maintaining and transmitting sound quality, they measure different aspects. The sampling rate determines the number of frequencies that can be captured when recording audio. Therefore, audio recorded at a lower sampling rate will have a lower frequency limit and limited range compared to audio recorded at a higher sampling rate.
Bit depth, on the other hand, determines the amplitude resolution of each sample. Therefore, for high-quality audio preservation, it is important to have both a reasonable bit depth and sampling rate. While 44.1 kHz is the standard for most common applications such as CDs, MP3s and streaming services, 24-bit depth is the optimal bit depth for professional audio.
Various bit depths
Bit depth can be thought of as the dynamic range for the amplitude or volume of an audio signal. The higher the bit depth, the more computing resources are required. Generally, 24-bit audio is considered optimal for human hearing, although the quality may improve when using 32-bit or even 64-bit audio.
There are also lower bit depths, such as 8- and 16-bit, but they are usually significantly inferior in quality. The difference between 16- and 24-bit audio is noticeable to the ear. Interestingly, “bitcrush” plugins specifically reduce the bit depth, creating a “low-quality audio” effect that can make you nostalgic for the old days.
What is the ideal sample rate and bit depth?
The ideal sample rate and bit depth depend on the size of your project. If you’re going to be recording music for digital streaming platforms like Spotify or Apple Music, recording at 24-bit depth and 44.1kHz sampling rate is the standard choice. For other types of projects, it’s important to know the optimal settings for your audio tracks in advance to avoid problems along the way. Ideally, the entire project should be done at the same sample rate to ensure consistent audio quality.
Tips and tricks for selective audio frequency
Use these basic audio principles to maintain audio quality during and after every session:
Maintain a constant sample rate
Regardless of the sample rate you choose for your audio session, it is important to keep it constant. Changing the frequency during operation can result in aliasing or aliasing artifacts, which appear as harsh distortions. These artifacts occur when the sampling rate is not high enough to accurately represent all frequencies in the audio spectrum. Therefore, for recordings with a high content of high-frequency sounds, it is recommended to select a higher sampling rate to avoid such problems.
Use 44.1 kHz as standard
When in doubt, use the 44.1 kHz sample rate as your base. This frequency allows you to cover the entire range of sounds perceived by the human ear. Depending on the nature of the composition, you may lose some high frequencies, so make decisions based on the specifics of your project. In any case, it is not recommended to use sampling rates below 44.1 kHz.
Check the intended output
Technically, there is no universal “ideal” sample rate, as it depends on the end-use requirements. If you are working with a new system or for a specific application, be sure to check the optimal specifications before you begin recording. This is also important when you plan to pass the audio to another person, such as a mixing engineer.
Audio sampling rate FAQ
Sampling rate determines the accuracy of digital audio, making it an extremely important aspect when recording. Here are some frequently asked questions and answers to help you through the analog to digital audio conversion process.
Can you hear the difference between 48 and 96 kHz?
To be honest, it is quite difficult to distinguish between 48 kHz and 96 kHz audio. However, a higher sampling rate can be useful for maintaining high audio quality over a long period of time.
Which is better – recording in 44.1 or 48 format?
Generally, the higher the sampling rate, the more detail can be captured. It’s optimal to record at 48 kHz to capture more of the nuances of the original sound. For professional recording, it is recommended to use a base frequency of 44.1 kHz, and ideally select a slightly higher sample rate.
What is the best sample rate for music?
Choosing the best sample rate for music applications depends on your audio goals. It is generally recommended to use a frequency of 44.1 kHz or higher to ensure that all elements of the original sound wave are accurately reproduced.
Why is sampling rate important?
Every time you convert analog audio to digital or process it through an audio interface, the audio is processed at a specific sample rate. A sample rate that is too low can significantly degrade audio quality, causing important details to be lost from the source material.
Maintaining a stable sample rate is essential when producing, designing, or recording music. While very high sampling rates can provide excellent quality, the size of files created at resolutions above 48 kHz may be impractical for everyday use.
For optimal quality, stick to a sample rate of 44.1 kHz or higher, and be sure to check the intended output signal before recording audio samples. Maintaining a constant sample rate throughout all stages of the music process will ensure a high quality final product. Good luck applying your new knowledge of sample rates!