Additive synthesis

Additive synthesis is a method of creating sounds using electronic hardware or software. It is one of several audio synthesis methods, along with subtractive synthesis, frequency modulation (FM synthesis), vector synthesis, and others.
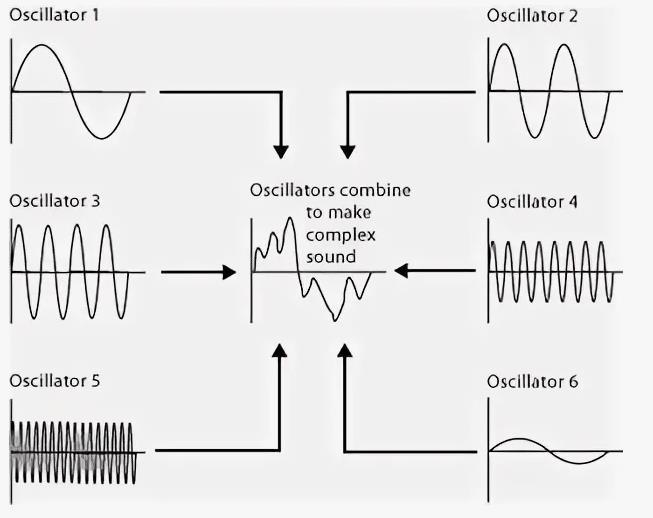
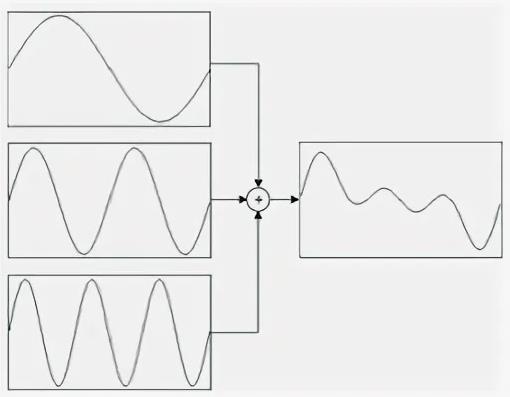
One common example of an additive synthesizer is the Kawai K5000 series, although there are many other additive synthesizers that we will discuss below. Additive synthesis works by summing multiple frequencies and amplitudes to create rich sound from sine waves. Simply put, additive synthesis adds together multiple sine waves to create sounds.
Musicians can use sine oscillators, harmonic settings, envelopes, noise, and other tools to transform these sine waves into a variety of sounds. By understanding additive synthesis, you will see how sine waves serve as the basis for many other familiar waveforms, such as sawtooth and triangle.
How does additive synthesis work?
Unlike other synthesis methods, additive synthesis starts with a completely blank slate. You then add sine waves with different characteristics and play them back simultaneously, with each new layer adding another degree of harmonics. In this process, each sine wave acts as an oscillator, since each layer influences the interaction between the previous and subsequent ones.
Additive synthesizers have envelope parameters that can be applied to individual sound waves or a group of selected sine waves. Because an organ layers sound sources on top of each other to then play as one instrument, it can be considered a type of additive synthesizer.
While additive synthesis allows for more precise control over the sound, it can be quite labor intensive depending on the number of layers required to create the final sound. Because of these limitations, software additive synthesizers are more common than hardware ones, although there are known examples of hardware versions.
With additive synthesis, you start practically from scratch, building a sound from a blank slate. In contrast, subtractive synthesis involves creating a rich sound with complex harmonics and then adjusting the waveform by removing unnecessary elements.
In subtractive synthesis, filters and envelopes are used to adjust the character of the waveform and suppress unwanted frequencies. Subtractive synthesis is much more common than additive synthesis. However, additive synthesis can provide more control over sonic character as you layer raw sounds on top of each other.
The Best Additive Synthesizers
1. Razor Native Instruments
Razor is an innovative additive synthesizer available in Native Instruments’ powerful modular Reaktor environment. With its intuitive interface and flexible modulation capabilities, Razor is capable of creating a wide range of sounds, from rich pads to aggressive leads.
Its unique additive engine allows you to manipulate up to 320 partial tones in real time, giving you precise control over the harmonic content of your sound. Razor offers multiple modules for each section, ranging from string-instrument-like modulation to creating otherworldly sounds as the modules interact with non-harmonic overtones in unique ways.
One of the notable aspects of Razor is its extensive modulation capabilities, including multiple LFOs, envelopes, and sequencers. These modulation options allow you to create dynamic, evolving sounds that respond to your playing or external cues.
Distinctive features:
- Up to 320 fragments for detailed sound processing;
- Wide selection of modules allowing creative influence on parts;
- Wide range of modulation options.
2. Loom II AIR Music Tech
Loom II is a powerful and easy-to-use additive synthesizer developed by AIR Music Tech. With a sleek, modern interface, Loom II offers a unique approach to additive synthesis, combining 30 editable modules to create impressive, evolving sounds.
Its modular architecture encourages experimentation, making it an excellent choice for electronic music producers and audio engineers. One of the distinguishing features of Loom II is the Morph Pad, which is rarely found in other additive synths. Morph Pad allows you to switch between different presets in real time, creating dynamic, evolving sounds that can be controlled with a MIDI controller or automated in your DAW.
Loom II also offers a range of built-in effects, including reverb, delay and distortion, which can be used to further enhance the sound, adding depth and character.
If you’re looking for the best reverb plugins of 2023, we also offer recommendations for the most popular options in the industry.
Distinctive features:
- Modular architecture of additive synthesis;
- Morph Pad for preset morphing in real time;
- Built-in effects.
3. Pigments 3 Arturia
Pigments 3 is a powerful synthesizer from Arturia that combines additive synthesis with other methods, including wavetable, virtual analog, granular synthesis and a multi-sample engine. With its powerful audio engine and intuitive interface, Pigments 3 is a comprehensive tool for modern music producers and audio engineers, offering a wide range of audio capabilities.
One of the standout features of Pigments 3 is its comprehensive modulation capabilities. These include multiple LFOs, multi-stage envelopes (MSEGs), random number generators, and a sequencer/arpeggiator. These modulation parameters provide a high level of control over the dynamics and movement of the sound, allowing you to create complex, evolving textures.
In addition, Pigments 3 offers a range of high-quality built-in effects, many of which are taken directly from Arturia’s analog plug-ins. These effects include filters, reverb, delay and multi-band compression, which can be used to further shape and enhance sounds.
Distinctive features:
- any synthesis methods, including additive;
- Comprehensive modulation capabilities;
- High-quality built-in analogue modeling effects;
- Full-featured sequencer/ARP with unique randomization capabilities.
4. Alchemy Logic Pro
Alchemy, included with Apple’s Logic Pro DAW, is a powerful synthesizer that combines additive synthesis with other methods, including granular, spectral, and virtual analog synthesis. It can load all of Logic’s patched samples (standard or custom) for further processing using any of these synthesis methods.
With extensive audio processing capabilities, Alchemy is a versatile tool for electronic music producers and audio engineers looking to create unique sounds. One of Alchemy’s standout features is its advanced spectral resynthesis capabilities, which allow you to analyze and recreate the harmonic content of existing sounds. This allows you to use real recordings or samples as the basis for your synth patches, offering a unique approach to sound design and synthesis.
Alchemy also has its own “morphology panel” which allows you to change preset parameters, which is not always possible in other additive synths. You can move between “scenes” in real time and use internal modulators to modulate each movement.
All Alchemy presets include these preset scenes, plus a unique feature: customize and save a preset, import it into Garageband iOS, and you’ll have full control over your preset’s pad!
Another notable aspect of Alchemy is its extensive modulation capabilities, including multiple LFOs, envelopes, and sequencers. These modulation options allow you to create dynamic sounds that respond to your playing or external signals.
Distinctive features:
- Many synthesis methods, including additive, granular, subtractive/VA and a full ESX-style multi-sample engine;
- Expanded capabilities of spectral resynthesis;
- Wide range of modulation capabilities;
- Morph Pad;
- Import iOS presets.
5. Harmor Image-Line
Developed by Image-Line, Harmor is a powerful additive synthesizer that offers a unique approach to sound design and synthesis. It combines a familiar subtractive interface with a powerful additive engine, making it an excellent choice for those new to additive synthesis.
Featuring an innovative resynthesis engine and intuitive interface, Harmor allows you to manipulate audio samples or create sounds from scratch using built-in additive synthesis capabilities. One of Harmor’s standout features is its advanced image resynthesis, which allows you to import images and convert their pixel data into audio. This feature offers a unique and creative approach to sound design, allowing you to create unique sounds based on visual data.
Harmor also provides a wide range of modulation options, including multiple LFOs, envelopes, and X/Y controllers. These instruments can be used to create dynamic, evolving sounds that respond to your playing or external influences.
Distinctive features:
- Innovative resynthesis engine;
- Advanced image resynthesis capabilities;
- Extensive modulation capabilities, including the famous IL custom envelopes;
- Can be used as a standard (but advanced) subtractive synthesizer.
Is FM synthesis additive?
No, FM synthesis and additive synthesis are different methods of audio synthesis. FM synthesis creates sounds by modulating the frequency and amplitude of one oscillator (carrier) with another oscillator (modulator). Additive synthesis, on the other hand, combines several individual sine waves to create a complex sound.
What is additive synthesis used for?
Additive synthesis is used to create sounds by layering different sine waves and playing them back simultaneously. This method allows for detailed control of harmonics and other parameters, creating unique sound textures.
How to create sound using additive synthesis?
Additive synthesis is created by superposing several sine waves. Each of these waves has its own characteristics, such as harmonics and envelopes, that add to the overall sound. An organ or pipe organ can be considered examples of additive synthesizers because they layer sound sources to create a complex sound.
What are the three main types of synthesis?
Although there are many subcategories of audio synthesis, three main groups include additive synthesis, subtractive synthesis, and frequency modulation synthesis (FM synthesis).
Understanding the intricacies of additive synthesis can be beneficial for any musician. Even if you don’t plan on devoting much time to complex sound design, creating your own unique instruments from scratch can be a fun and creative process.